Dysphagia treatment in Mumbai
Dysphagia is the medical term of swallowing difficulties. Swallowing becomes difficult because the muscles responsible for chewing and swallowing become uncoordinated. As a result, whatever you eat or drink goes down the wrong way and some times reaches the lungs instead of stomach (micro aspiration). This causes chest infections and even pneumonia in some cases. Dr. Vedant Karvir is one of the best gastroenterologist in Malad. He offers the advance Dysphagia Treatment in Mumbai
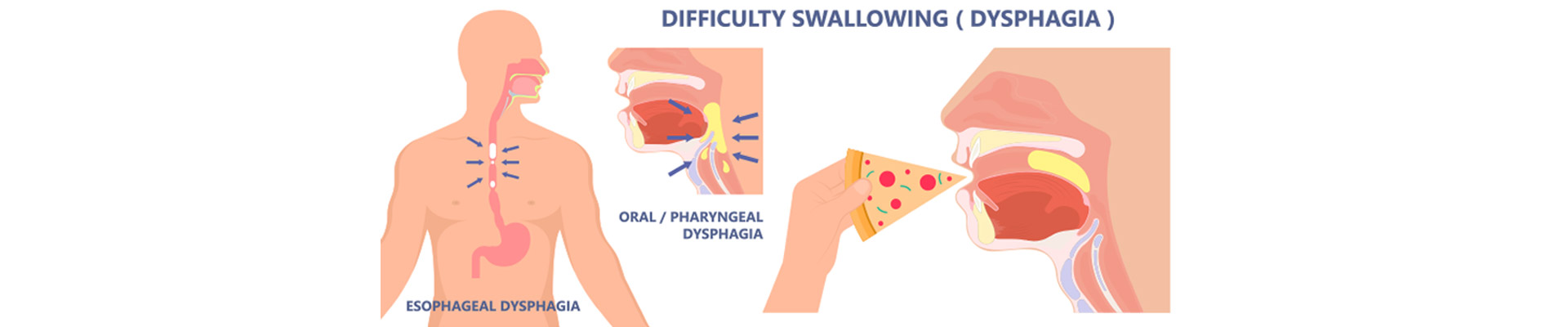
Types of dysphagia
There are three main types of dysphagia:
- Oropharyngeal dysphagia– in oral dysphagia, one has difficulty in chewing and swallowing the food. It is generally caused due to neurological disorders such as a stroke, parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis etc
- Esophageal dysphagia – esophageal dysphagia is caused because of narrowing, scarring or blocking of the esophagus. One feels as if the food is stuck in the throat or chest. Conditions such as gerd and barrett’s disease are the main cause of esophageal dysphagia.
Symptoms of dysphagia
- Hoarseness
- Choking while eating
- Unintentional weight loss
- Regurgitation
- Recurrent heartburn
- Gagging
Causes of dysphagia
- Neurological degeneration
- Stroke
- Esophageal ring
- Multiple sclerosis
- Radiation
- Esophageal stricture
- Esophageal cancers
Complications associated with dysphagia
- Dehydration- difficulty in eating and drinking fluids may lead to dehydration as the body does not get enough fluids.
- Malnutrition – a person suffering from dysphagia, especially if it has not been diagnosed, does not get the right amount of vital nutrients needed by the body to remain healthy.
Diagnosis is by endoscopy & esophageal manometery. Contact us for advance Dysphagia treatment in Mumbai at globus Hospital.
To book an appointment with Globus Hospital call on 98331 06104, 98331 87118 or visit our hospital at 201, Second Floor, Kothari Milestone Mall, Near Natraj Market, S.V Road, Malad West - 400064. For hospital directions click here.